What Is the Stock Market & How Does It Work?
If you’ve ever watched financial news or checked your retirement account, you’ve likely wondered, what is the stock market? The stock market is a system that allows individuals and institutions to buy and sell ownership in publicly traded companies. While it may seem complex at first, understanding stock market basics can help you know how wealth is created and how the economy functions.
What Are Stocks?
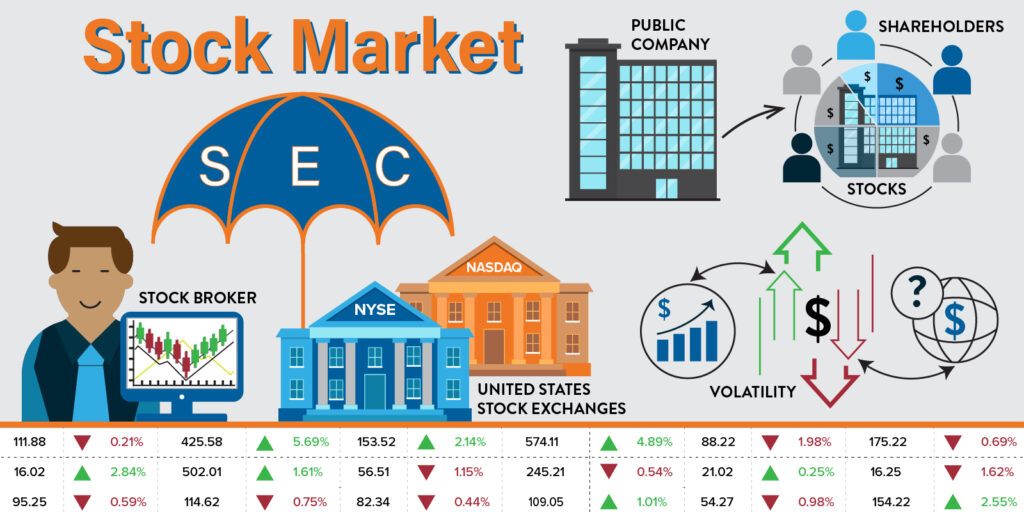
To understand the stock market, it’s important to first answer the question: what are stocks? A stock represents a share of ownership in a company. When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder, meaning you own a small piece of that business. Companies issue stocks to raise capital for growth, operations or innovation. While investors buy stocks in hopes of earning a return through price appreciation or dividends.
What Does the Stock Market Do?
So, what does the stock market do? It serves as a marketplace where buyers and sellers meet to trade stocks. Major U.S. stock exchanges include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the Nasdaq. These exchanges provide structure, transparency and regulation, ensuring that trades occur fairly and efficiently. Beyond trading, the stock market helps allocate capital across the economy, supporting business expansion and job creation.
Stock Market Basics: How It Works
Stock market basics revolve around supply and demand. When more people want to buy a stock than the amount of people that are selling it, the price rises. When more people want to sell than buy, the price falls. Trades are executed electronically through brokers, which are either online platforms or financial professionals acting on an investor’s behalf. Market indexes like the S&P 500 or Dow Jones Industrial Average track the performance of groups of stocks, offering insight into overall market trends.
Why Do Stocks Go Up and Down?
A common question investors ask is, why do stocks go up and down? Stock prices fluctuate due to a variety of factors, including company earnings, economic conditions, interest rates and investor sentiment. Strong profits or new products can drive prices higher, while negative news or economic uncertainty can push prices lower. These movements reflect changing perceptions of a company’s future value.
Who Regulates the Stock Market?
You may also wonder, who regulates the stock market? In the United States, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) oversees the market. The SEC enforces laws designed to protect investors, maintain fair markets, and ensure transparency. Exchanges and brokerage firms are also subject to strict rules to help prevent fraud and market manipulation.
Why the Stock Market Matters
Understanding what the stock market is helps investors make informed decisions and participate more confidently in long-term financial planning. While investing involves risk, the stock market has historically played a key role in building wealth and supporting economic growth.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to expand your knowledge, learning how the stock market works is a valuable step toward financial knowledge.
If you’re looking for more financial education, check out our blogs.

